Manufacturing
Ready-to-press and sinterable silicon carbide (RTP SiC) granules
Overview
Ready-to-press silicon carbide (RTP SiC) granules is being produced using spray drying or spray freeze drying technique through an intermediate colloidal processing route. This method is capable of producing different size spherical granules with narrow size distribution and improved flow characteristics. As the granules are produced from uniformly dispersed slurries of SiC powder, hence wide range of additives can be accommodated in the formulation of the RTP granules. This process is beneficial to manufacture the feedstock for producing green SiC compacts with high density, defect free homogenous microstructure. The sintered products thus produced exhibit superior properties than conventionally produced SiC. The technique has been adapted to produce RTP granules comprising water sensitive nitride based composite powders.
Key Features
- Cost effective technique to produce RTP SiC granules.
- Flexibility to incorporate either solid-state or liquid-phase sintering additives in the formulation of RTP granules.
- Control on granule size with narrow distribution
- The process can be adopted for manufacturing various oxide or non-oxide ceramics.
- Up to 97.8 % relative density achieved in the sintered parts.
Potential Applications
- Feedstock for manufacturing of high performance SiC, Si3N4, SiAlON components
Intellectual Property Development Indices (IPDI) 
- RTP granules processed in the laboratory scale
- Scaling up the process is in progress
| Status | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
Major Patents / Publications
Major Patents
Major Publications
- P. Barick, B. P. Saha, S. V. Joshi and R. Mitra, Spray-freeze-dried nano-crystalline SiC containing granules: processing, compaction behaviour and sintering, J. Euro. Ceram. Soc., 36 (2016), 3863-3877
Dense silicon carbide (SiC) coatings by chemical vapour deposition (CVD) technique
Overview
Theoretically dense SiC coating processed by chemical vapour deposition (CVD) exhibits superior physical, mechanical, thermal and optical properties with excellent wear, abrasion and chemical corrosion resistance. The properties of CVD SiC coating can be tailored by control of various parameters including reactor design, process temperature, pressure, reactants composition and flow geometry. ARCI has established a CVD system for coating of large size components (up to 1.0 m meter) by thermal deposition of methyl-trichlorosilane (MTS) in excess of hydrogen. High density CVD SiC coating on various substrates with different geometries have been produced. It has been demonstrated that the CVD SiC coating can be polished up to the RMS surface roughness < 1 nm. ARCI also has the capability to produce self-standing CVD SiC parts.
Key Features
- State-of-the art CVD SiC coating facility.
- The processes technology has been established
- SiC coating on different size and shapes can be produced.
- CVD SiC coating can be polished to very high surface finish(<1 nm).
Potential Applications
- Reflectors for high energy laser and synchrotron radiation.
- Wear and corrosion resistant coatings
- Reflectors for concentrated solar power (CSP) applications
- Solar collectors and concentrators for astronomical telescopes.
Intellectual Property Development Indices (IPDI) 
- The process technology and repeatability have been established.
| Status | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
Major Patents / Publications
Major Patents
Major Publications
Exfoliated graphite and its value-added products
Overview
The stacked parallel layers in natural graphite flakes (NGF) are separated by 0.34 nm and the layers in a stack are attached or bonded with a weak Van der waal forces. For successful exfoliation, overcoming the van der Waal attraction between the adjacent layers is crucial. The best feasible method is to decrease the attractions by increasing the distance between the adjacent layers via oxidation and chemical intercalating reactions. During oxidation of graphite, the functional groups like hydroxyl, epoxide and hydroxide etc are inserted between the layers leads to increase in d-spacing from 0.34 to 0.70 nm. Due to thermal shock, the functional moieties try to escape and create porous structure is termed as exfoliated graphite (EG). EG can be moulded into various desired shapes (sheets, tapes, seals, and boards) by mechanical compaction without adding any sort of binders. Self-binding capability of the porous-structured material is a unique characteristic of this technology. Our technology demonstrates the production of EG in bulk quantity by chemical intercalation and thermal exfoliation of NGF. It is a cost-effective and continuous process for bulk production.
Key Features
- Binder-free compaction of material
- Shape-tailored material
- Very light weight
- Density-controlled compaction
- Sandwich or reinforced material with better mechanical properties
- Efficient and cost-effective
Potential Applications
- Flexible sheets
- Flexible tapes
- Bipolar plates
- Seals
- Reinforced seals, sheets and tapes etc
- Ultra light weight boards
Intellectual Property Development Indices (IPDI) 
- Scale-up and pilot plant is established
- Demonstration of bulk quantity through thermal reactor is done
- Various types of prototype module has been established
| Status | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
Major Patents / Publications
Major Patents
Major Publications
Refurbishment of Cast Iron Components using Laser Cladding
Overview
Grey cast iron finds extensive applications in the Glass mould industries and automotive industries for making of components like dies, gears, links, cylinder block, cylinder head, clutch plate etc. Many times, the size of the cast component is large and a small localize wear can lead to scrapping the entire component. Repair of cast iron has been very challenging due to presence of free carbon in the form of graphite flakes which forms COx gases during deposition and these gases get entrapped during the deposition process resulting in porosity. Transverse cracking is another deterrent in repair which occurs due to interfacial stresses associated with formation of hard and brittle heat affect zone. Laser cladding due to its advantages like minimal and controlled energy input can minimise the heat affected zone and minimise the formation of COx gases. Repair solutions with or without pre-heating were developed successfully.
Key Features
- Negligible porosity
- Crack free deposition
- No distortion
- Minimal heat affected region
Potential Applications
- Glass Mould Dies
- Cylinder Heads
- Cam Shafts
- Gear Boxes
- Heavy engineering equipment and machine beds
Intellectual Property Development Indices (IPDI) 
- Performance and stability are validated at laboratory scale
- Prototypes are generated
- Field trials are underway
| Status | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
Tungsten fibre reinforced tungsten composites by spark plasma sintering
Overview
Tungsten has extensive usage in strategic applications. However, it’s application is limited to a great extent due to lower toughness and this can be improved by incorporating new ductile phases and fibres into the tungsten matrix. Tungsten fibre reinforced tungsten (Wf-W) composite is developed at ARCI to overcome brittleness issues in tungsten. This work involves spark plasma sintering of Wf-W composites using bare and oxide-coated tungsten mesh of 100 µm diameter stacked as alternate layers between the tungsten powders. An optimum volume fraction of Wf is envisaged to yield at least double the fracture toughness of pure tungsten, alongside high thermal conductivity and good high temperature mechanical properties such as UTS, YS, fracture strength and elongation. Detailed microstructural and mechanical property investigations were carried out to validate the concept of extrinsic toughening in such composites.
Key Features
- Fabricated with Wf weight fraction up to 10%
- Density: ≥ 18 g/cc obtained with grain size: ≤ 20 µm
- Hardness: > 400 HVN and thermal conductivity ≥ 150 w/MK achieved
- Process can be scaled up for commercial applications
- Alternate PM based route for fabricating Wf-W composites
Potential Applications
- Plasma facing components
- High temperature applications
Technology Readiness Level (TRL) :
- Processing and property evaluation on at laboratory scale
Intellectual Property Development Indices (IPDI) 
- Basic concepts and understanding of underlying scientific principles
- Short listing possible applications
- Research to prove technical feasibility for targeted application
| Status | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
Major Patents / Publications
Major Patents
Major Publications
Nano fertilizer by Cryo-milling
Overview
Nano fertilizers are emerging as new generation fertilizers for low dosage, soil restoration, conservation of phosphorous nutrients, and reduction in imports. The nano Di-ammonium phosphate fertilizer (n-DAP) is developed and its efficacy is demonstrated successfully at the lab level. The n-DAP was prepared by a novel cryo-milling process at ARCI without altering the chemical structure, and tested at University of Hyderabad. Nano-sized DAP produced at ARCI has a particle size 5000 times lesser and specific surface area 14000 times greater than that of commercially available DAP (C-DAP). The n-DAP enhanced the growth of monocot (wheat) and dicot (tomato) plants. The improved agronomic factors such as higher leaf biomass, longer shoot, shorter root, and extraordinary efficacy were observed with n- DAP for 75% lesser input than C-DAP.
Key Features
- New solution to reduce the excessive use of fertilizers in agriculture.
- Production of n-DAP by cryo-milling process
- Better performance.
- Higher efficacy
- Plant requires 75% lesser dosage than commercial DAP
- Feasible process for up scaling
Potential Applications
- Agriculture sector
Technology Readiness Level (TRL)
- Processing and properties are validated at laboratory scale
- Pilot scale production is under progress
Intellectual Property Development Indices (IPDI) 
- Basic concepts and understanding of underlying scientific principles
- Short listing possible applications
- Research to prove technical feasibility for targeted application
| Status | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
Major Patents / Publications
Major Patents
- 1 Singh NRR, Sreedhara SudhakaraSarma, Tata Narsinga Rao T, Pant H, Srikanth VVSS, and Kumar R* (2021) Cryo-milled nano-DAP for enhanced growth of monocot and dicot plants. Nanoscale Advances, 3, 4834 – 4842
Major Publications
Powders for Additive Manufacturing
Overview
Key Features
- Powder requirements are currently being met through imports and powders are expensive.
- Gas atomizer produces wide variety of powders for various applications.
- Narrow fraction of powders taken after sieving based on the AM process.
- A contribution to “Make in India” program of the government of India.
Potential Applications
- Automobile
- Biomedical
- Aerospace
- Defence
Technology Readiness Level:
- Synthesis of powder (in 10 kg batches) demonstrated.
- Components are being made by AM
Intellectual Property Development Indices (IPDI) 
- Basic concepts and understanding of underlying scientific principles
- Short listing possible applications
- Research to prove technical feasibility for targeted application
- Coupon level testing in stimulated conditions
| Status | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
Major Patents / Publications
Major Patents
Major Publications
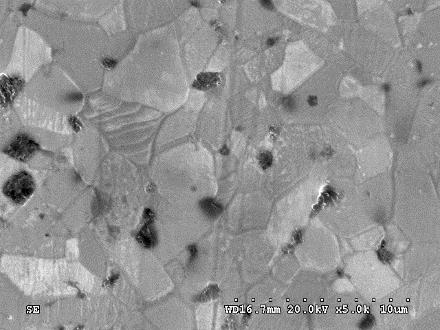
Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Austenitic Steels for High Temperature Applications
Overview
Oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) austenitic steels are endowed with high temperature strength and resistance to creep, fatigue, oxidation and hot corrosion. Hence, these steels are potential candidates for the ultra-super critical steam turbines, which are exposed to temperatures of about 700 C. The high temperature properties of ODS steels are due to the fine-grained microstructure, stable nano sized oxide(Y-Ti-O complex) dispersoids and stability of the microstructure at high temperatures. ARCI has embarked on major program for development and demonstration of technologies for the manufacture of blades for ultra-super critical steam and gas turbines.
Key Features
- High operating temperature of 650-700 °C
- High yield strength of 300 MPA at 700° C
- Good oxidation resistance
- Potential candidates to replace nickel based super alloys
Potential Applications
- Blades for ultra-super critical steam turbines
- High pressure compressor and low pressure turbine blades of gas turbines
- Other high temperature applications
Technology Readiness Level:
- Established manufacturing processes at pilot scale
- Performance and stability validation at prototype level underway
Intellectual Property Development Indices (IPDI) 
- Basic concepts and understanding of underlying scientific principles
- Short listing possible applications
- Research to prove technical feasibility for targeted application
- Coupon level testing in stimulated conditions
| Status | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
Major Patents / Publications
Major Patents
- S. Ganesh, P. Sai Karthik, M. Ramakrishna, A.V. Reddy, S.B. Chandrasekhar, R. Vijay, “Ultra-high strength oxide dispersion strengthened austenitic steel”, Materials Science and Engineering A, 814 (2021) 141192.
- P.S. Ninawe, S. Ganesh, P. Sai Karthik, S.B. Chandrasekhar, R. Vijay, “Microstructure and mechanical properties of spark plasma sintered austenitic ODS steel”, Advanced Powder Technology, 33 (2022) 103584.
- P. Sai Karthik, S. Ganesh, P. S. Ninawe, M. Battabyal, S. B. Chandrasekhar, R. Vijay, “Microstructure and mechanical properties of austenitic ODS steel processed using Ni–20Cr”, Journal of Materials Research, DOI:10.1557/s43578-023-00938-6, 2023